High blood pressure otherwise known as hypertension, is a circulatory disease. All parts of the body depend on the circulation, and many organs suffer from the impact of untreated hypertension. One of the organs at greatest risk is the brain.
When you hear the words “high blood pressure” your first association might be with the heart. But do you know your brain, with its constant need for oxygen and nutrients, is also extremely vulnerable.
In this blog post, we will discuss what high blood pressure is, why it’s important to keep your blood pressure under control, and how high blood pressure can specifically affect the brain.
What is high blood pressure?
Blood pressure is the force of your blood against the walls of your arteries and is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
Learn what’s considered normal, as recommended by the American Heart Association.
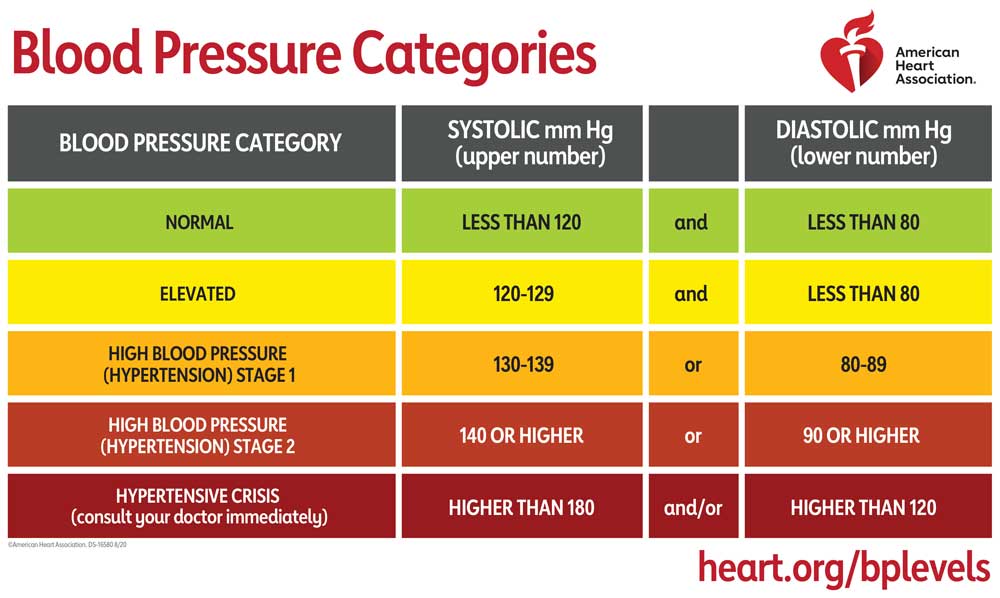
If you have high blood pressure, it means that your heart is working harder than it should to pump blood through your body. This can lead to a variety of health problems, including stroke, heart attack, heart failure, and kidney disease. That’s why it’s so important to keep your blood pressure under control!
High blood pressure increases your risk of stroke.
Stroke is one of the scariest consequences of having high blood pressure. High blood pressure can weaken or damage your blood vessels, which can cause them to leak or even burst inside your brain.
Depending on what part of your brain loses blood and what it does, you could have problems with language, vision, movement, or anything else your brain controls. It could be temporary if the blood flow is restored, or the damage may be permanent if the cells die. A stroke can also influence:
- your speech and language abilities
- your memory
- your mental health
High blood pressure increases your risk of developing dementia.
Many researches show a link between cognitive decline and high blood pressure. Damage to blood vessels carrying oxygen to the brain, can interfere the healthy flow of blood to the brain. When brain cells are deprived of oxygen and nutrients, you will start to show signs of cognitive impairment.
Hypertension does increase your risk of mild cognitive impairment, but more importantly, it can increase your risk of developing more serious conditions, such as vascular dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, later in life.
How can I lower my blood pressure?
Research has found that lowering your blood pressure by even 10 mm/Hg decreases the risk of stroke by 44%.
There are a number of things you can do to lower your blood pressure and keep it under control. These include:
- eat a healthy diet
- regular exercise
- quitting smoking
- reducing stress
- reduce salt (sodium) in your diet
- get a good night’s sleep
In conclusion
Hypertension contributes to both early cerebrovascular brain ageing and cognitive decline. It is a serious condition that can lead to stroke, mental decline, and dementia. It’s important to keep your blood pressure under control by eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and reducing stress. By following these tips, you can lower your blood pressure and protect your health!
Source/s:
Banner Image by Freepik.com
Blood Pressure Chart by American Heart Association